Initial Configuration
Configuring the SMTP Relay
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-configIn the main menu, select 'SMTP':

Specify IP address or the DNS name of the SMTP relay and validate:

The Postfix configuration is updated:

Exit the configuration utility and restart the Postfix service with the following command:
$ systemctl restart postfix
Configuring the Horizon Administrator’s Email Address
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-configIn the main menu, select Administrator:
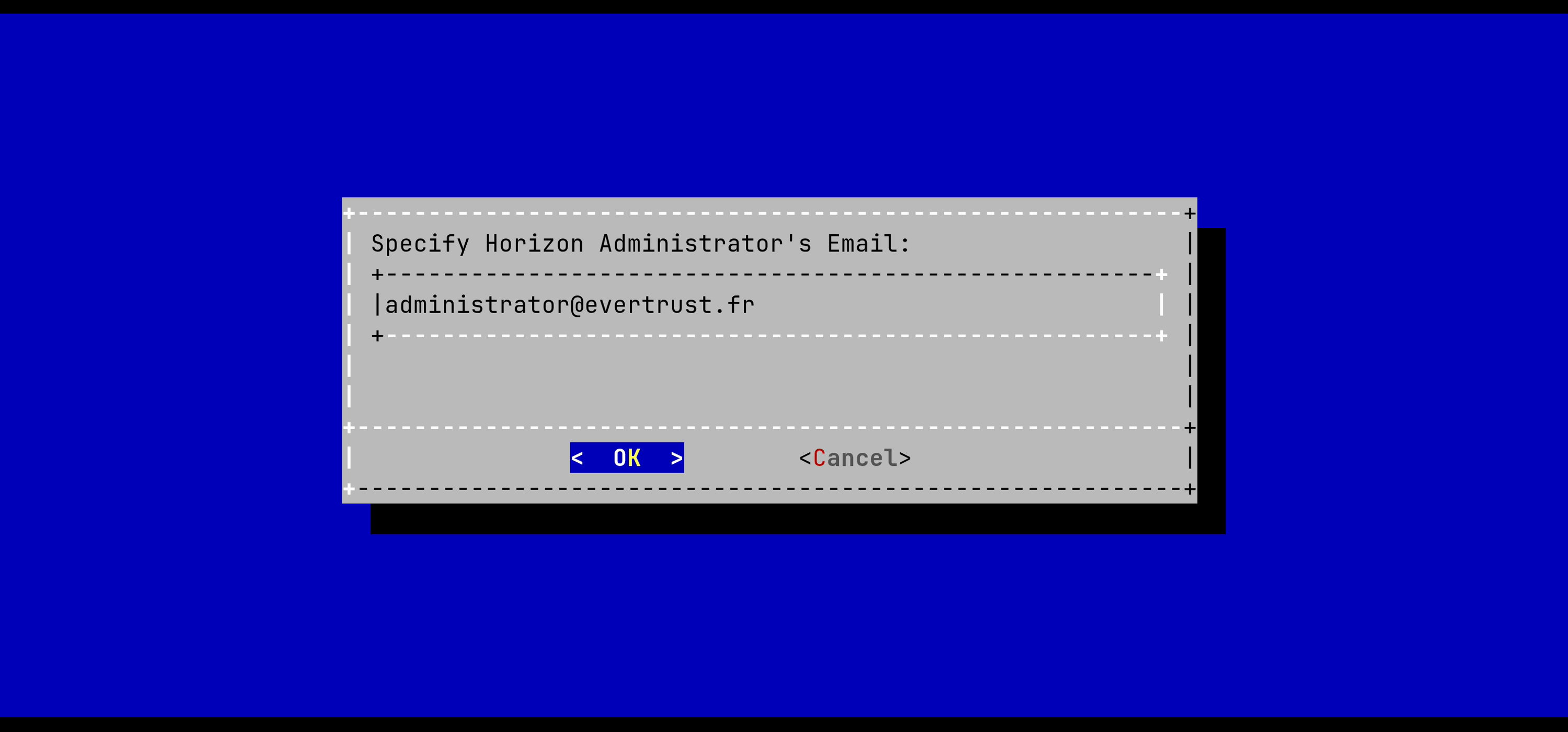
Specify the email address of the Horizon Administrator and validate:
Exit the Configuration Utility;
Validate the SMTP relay and Administrator Email Address with the following commands:
$ yum install mailx $ mail -s "Hello Horizon root" > Hello From Horizon .
Ensure that the email receives the test email.
Generating a new Horizon Application Secret
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-configIn the main menu, select 'Pekko_Play':
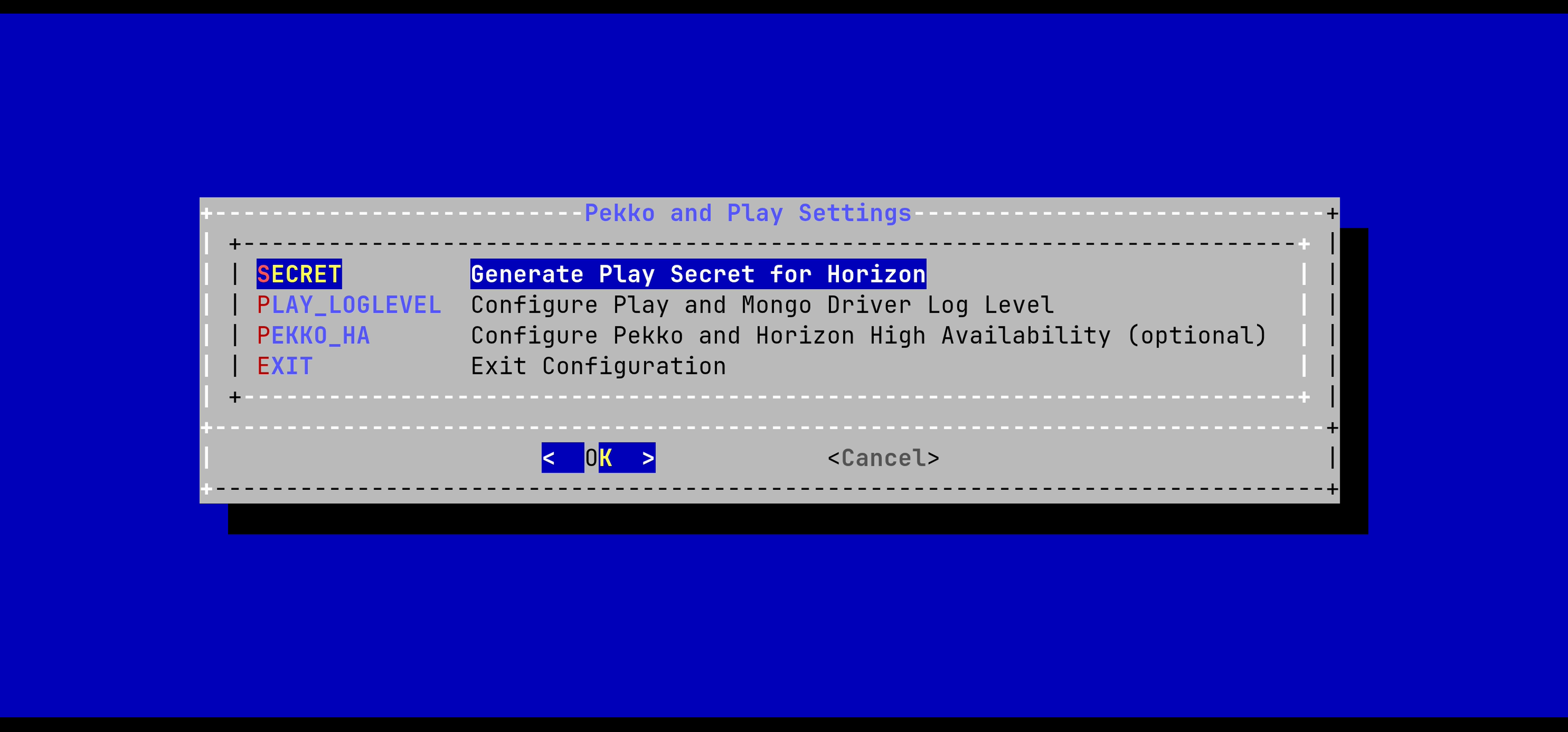
In the Pekko_Play menu, select 'SECRET':
Validate the new Horizon Application Secret:
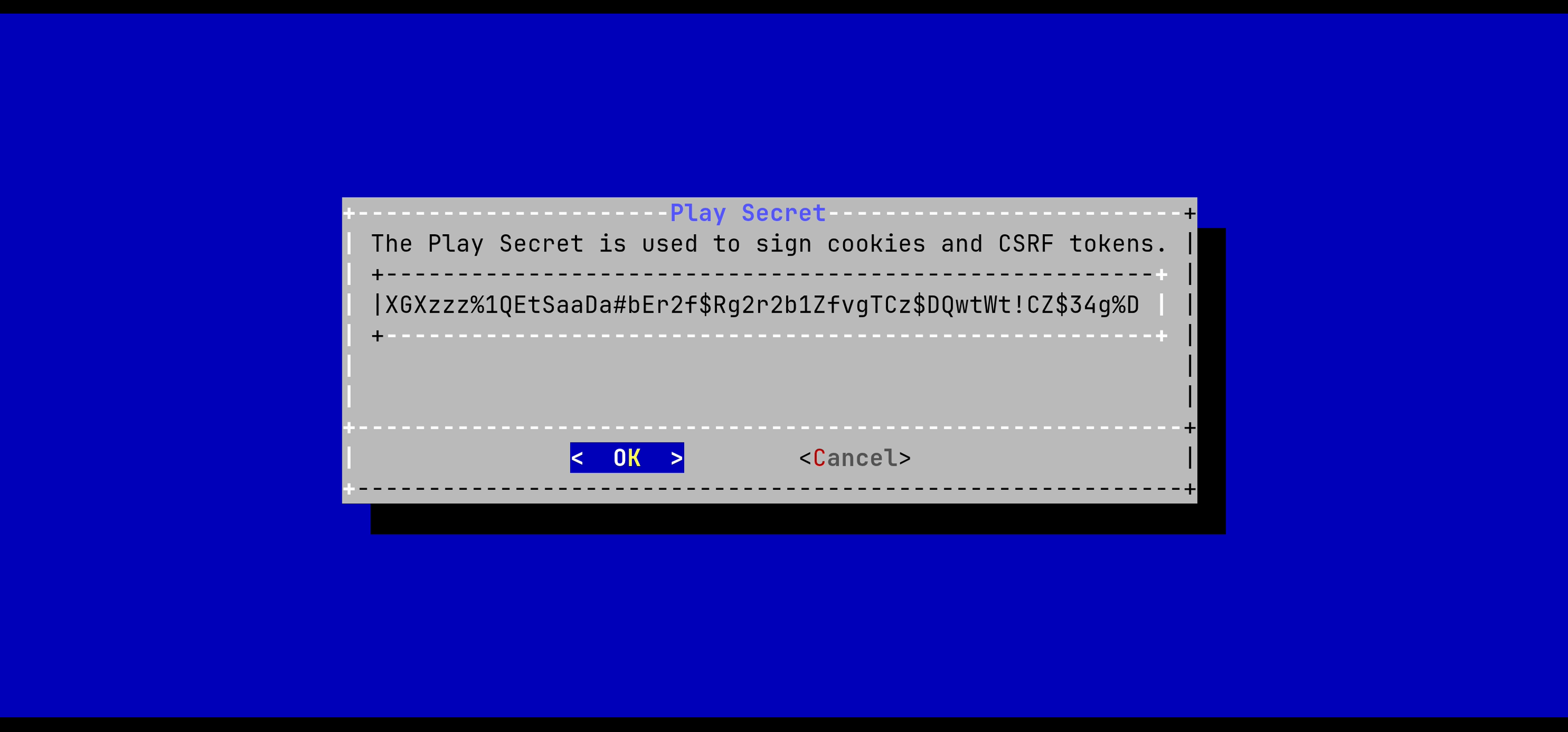
The Horizon configuration is updated:
For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonJVM Configuration
Horizon allows you to configure the xms (minimum memory allocation pool) and xmx (maximum memory allocation pool) parameters of the JVM running Horizon using the configuration tool.
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-configIn the configuration menu, select 'Horizon':

In the Horizon configuration menu, Select 'JVM':

Specify the 2048 for xms and 3072 for xmx parameters and select 'OK':

The new JVM parameters are configured:

For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonMongoDB URI Configuration
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-configIn the main menu, select Horizon:

In the Horizon configuration menu, Select MONGODB_URI:

Specify the MongoDB URI to target your MongoDB instance:

|
Horizon is installed to target a local MongoDB instance by default. If you use an external MongoDB (such as MongoDB Atlas Database or dedicated On-premises database) instance:
External MongoDB database URI syntax:
External MongoDB cluster of databases URI syntax:
|
The MongoURI is configured:
For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonHorizon Hostname Configuration
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-configIn the main menu, select 'Horizon':
In the Horizon configuration menu, select HORIZON_HOSTNAME:

Specify the DNS FQDN by which Horizon will be accessed:
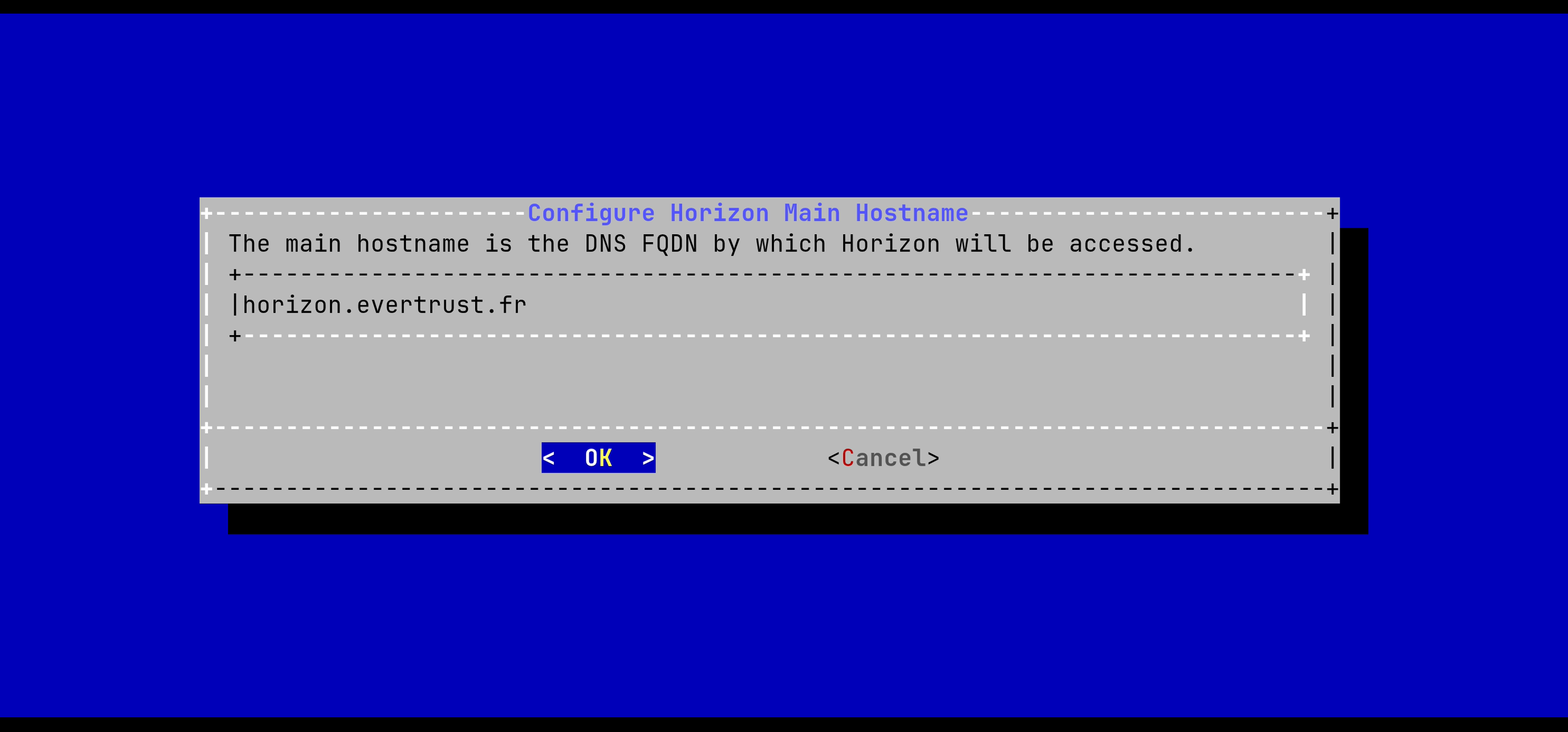
The Horizon Hostname is configured:
For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonGenerating an event seal secret
Horizon will generate functional events when using the software.
These events are typically signed and chained to ensure their integrity. Therefore, you must specify a sealing secret for this feature to work correctly.
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-configIn the main menu, select 'Horizon':

In the Horizon menu, select 'HORIZON_SEAL_SECRET':

Validate the new event seal secret:
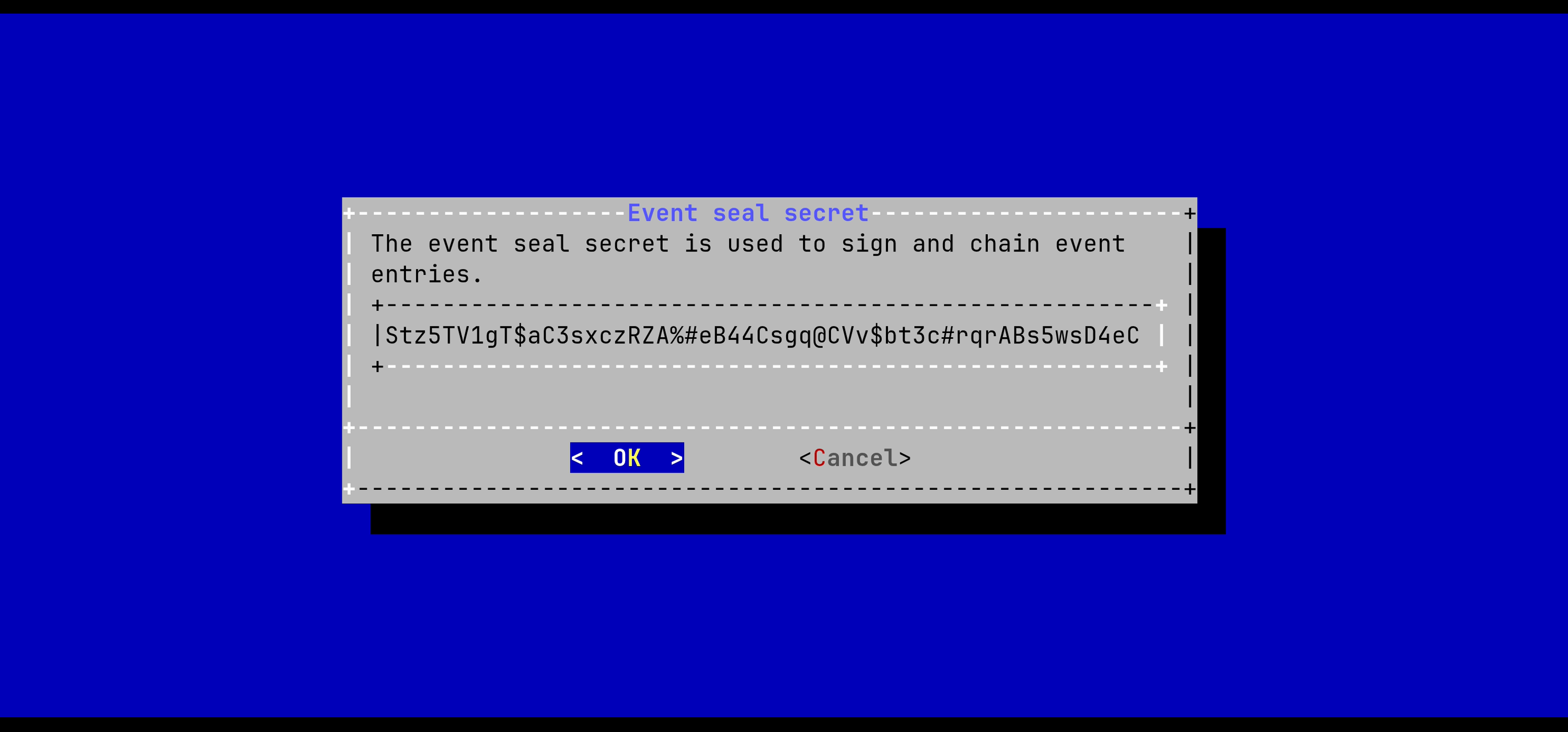
The event seal secret is now configured:
For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonInstalling the Horizon license
|
You should have been provided with a 'horizon.lic' file. This file is a license file and indicates:
|
Upload the horizon.lic file through SCP under /tmp/horizon.lic;
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-configIn the main menu, select 'Horizon':
In the Horizon configuration menu, Select 'HORIZON_LICENSE':
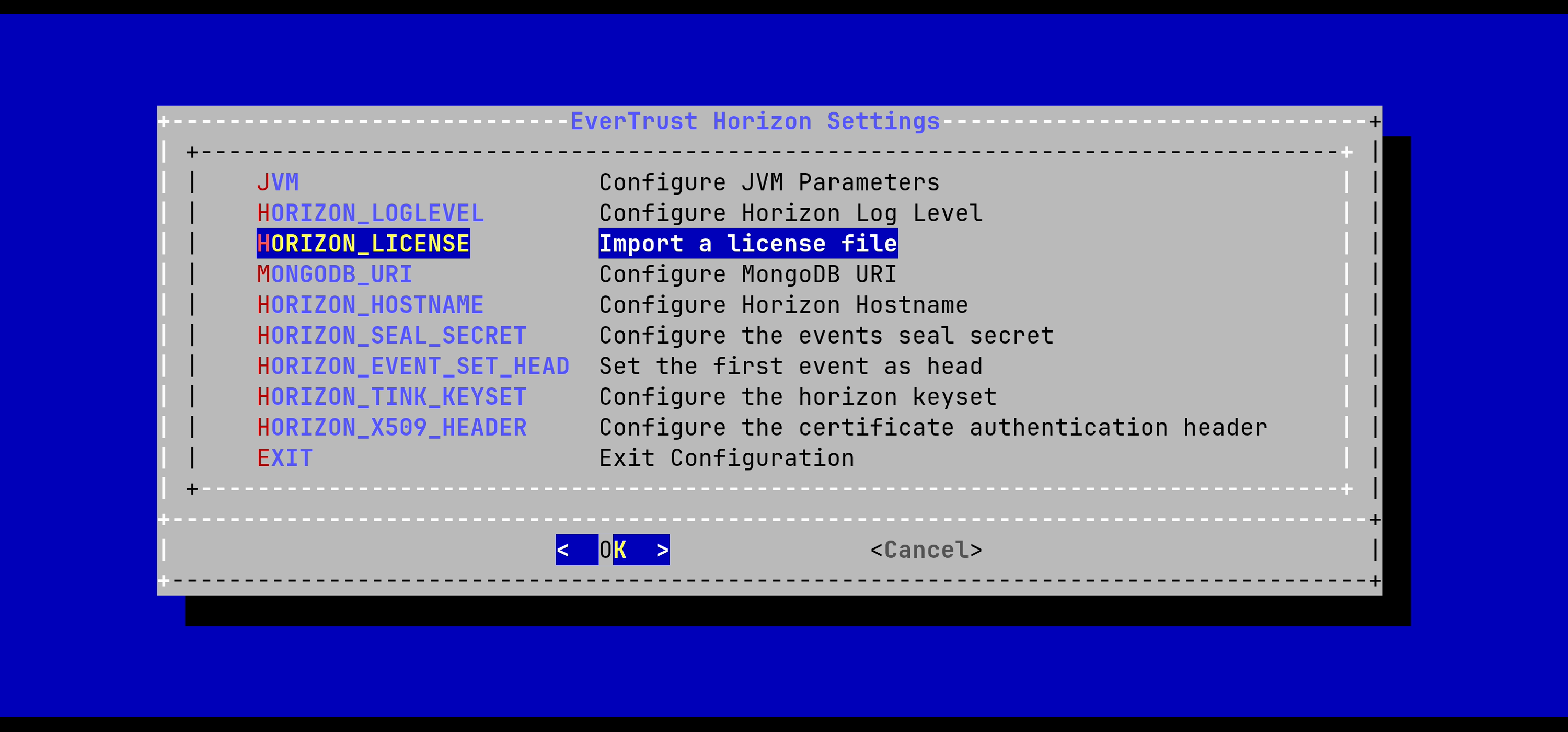
Specify the path /tmp/horizon.lic and validate:
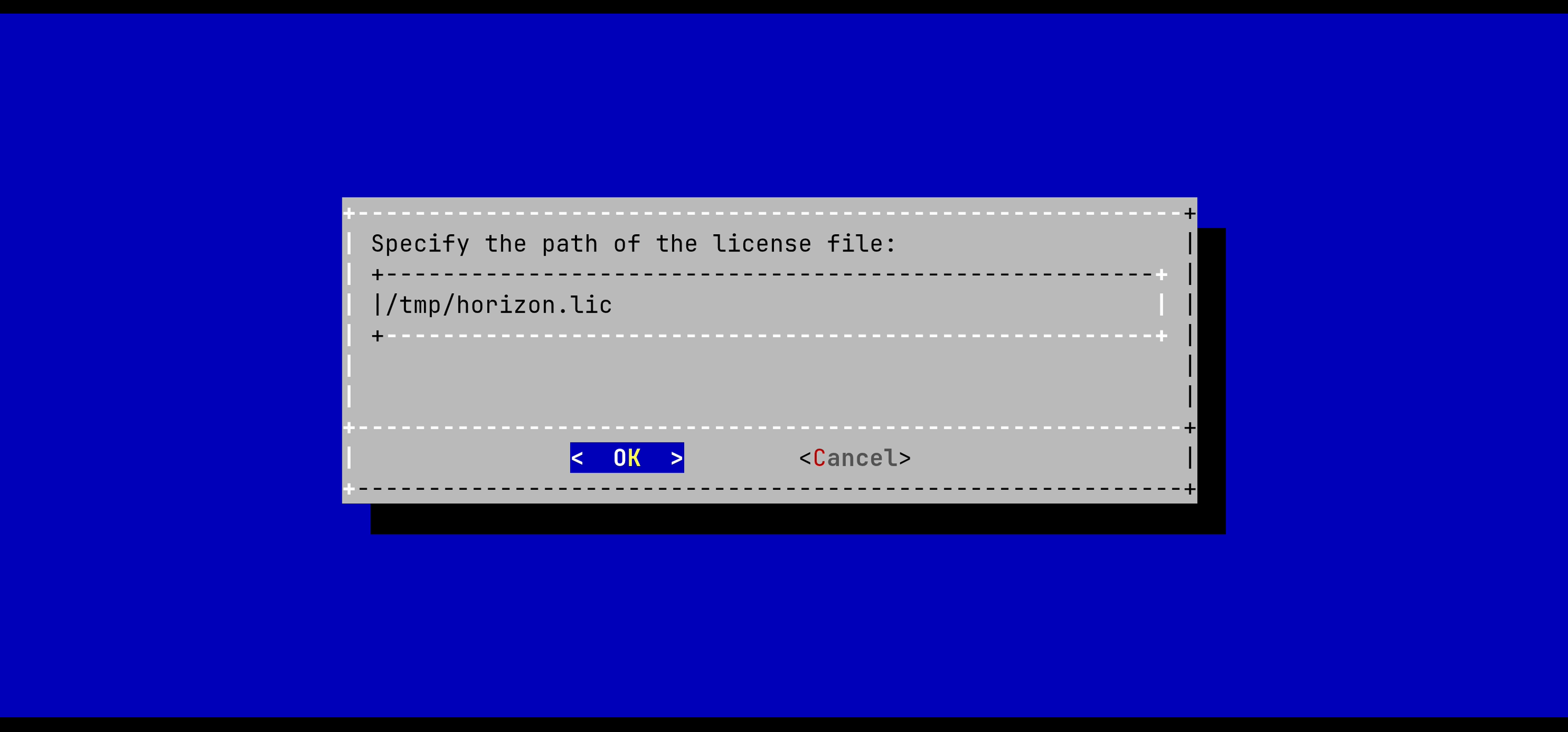
The information of the license should be prompted. If everything is good, import the license:
The Horizon License is configured:
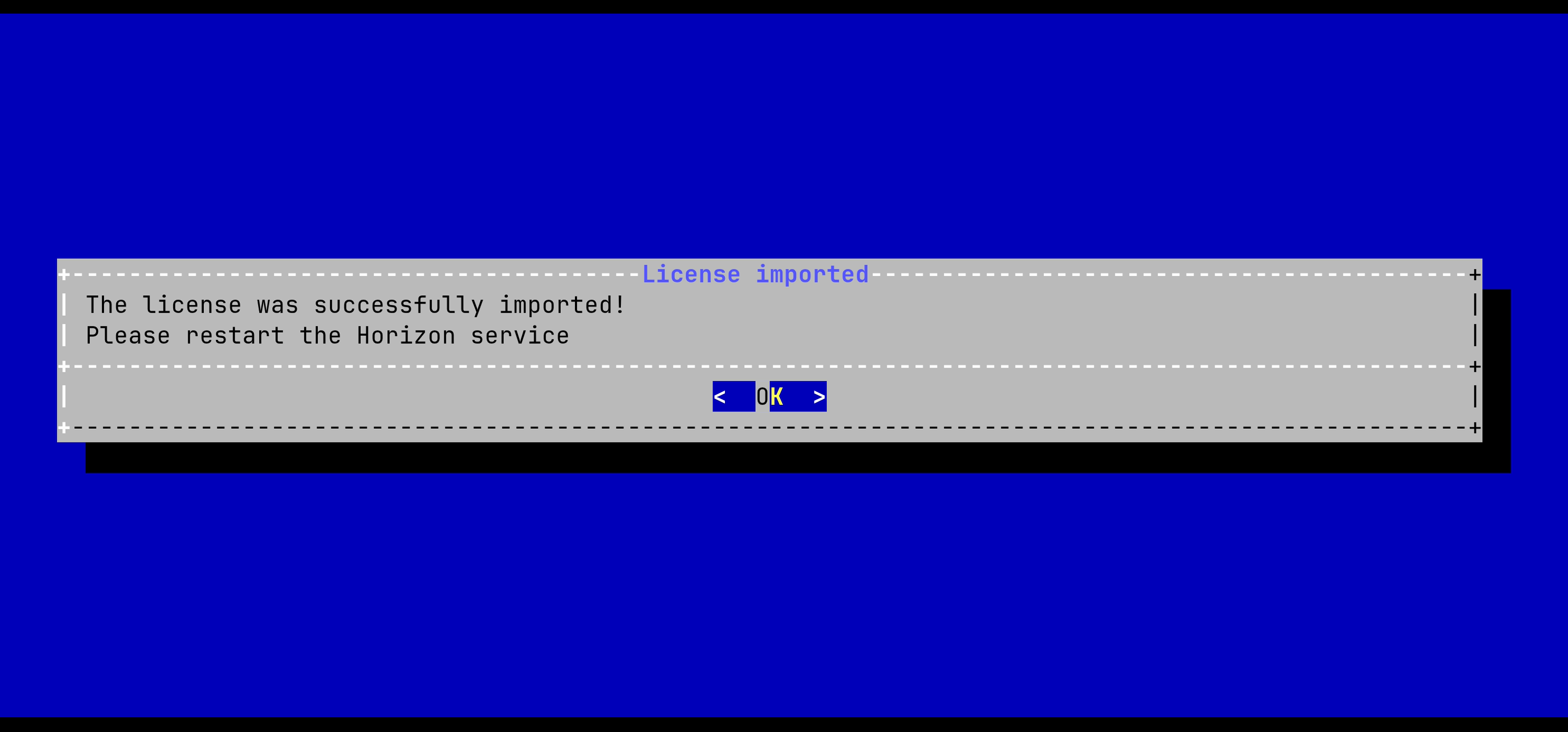
For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonGenerating a Tink keyset
To protect its secrets, Horizon relies on Tink. A Tink keyset can be issued as:
-
A plaintext keyset (stored as a file, protected by the filesystem rights and SELinux);
-
A GCP keyset (protected by a master key in a GCP KMS);
-
An AWS keyset (protected by a master key in an AWS KMS).
-
A PKCS#11 keyset (protected by a master key in an HSM).
| In order to generate a keyset, the Tinkey tool must be installed. |
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-configIn the main menu, select 'Horizon':
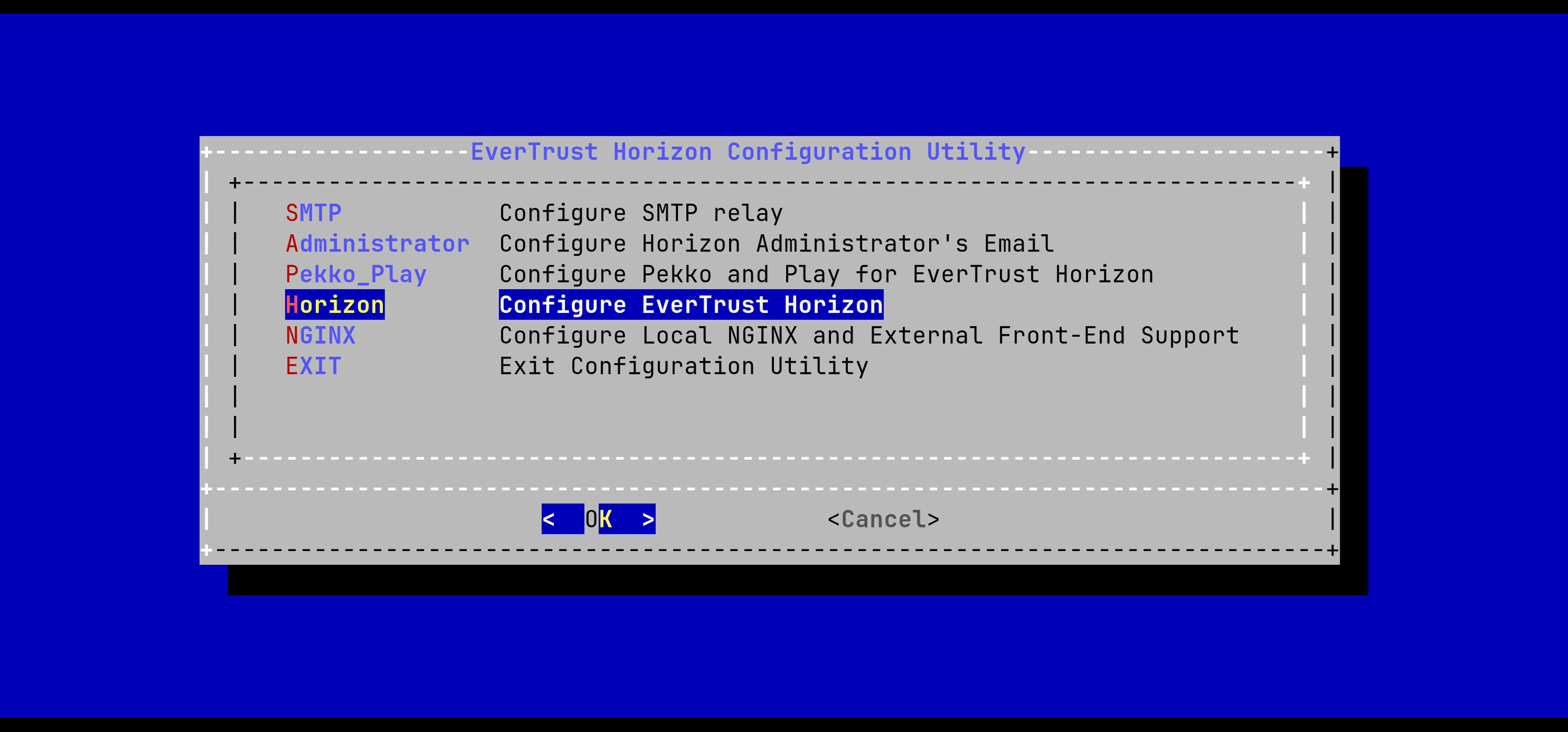
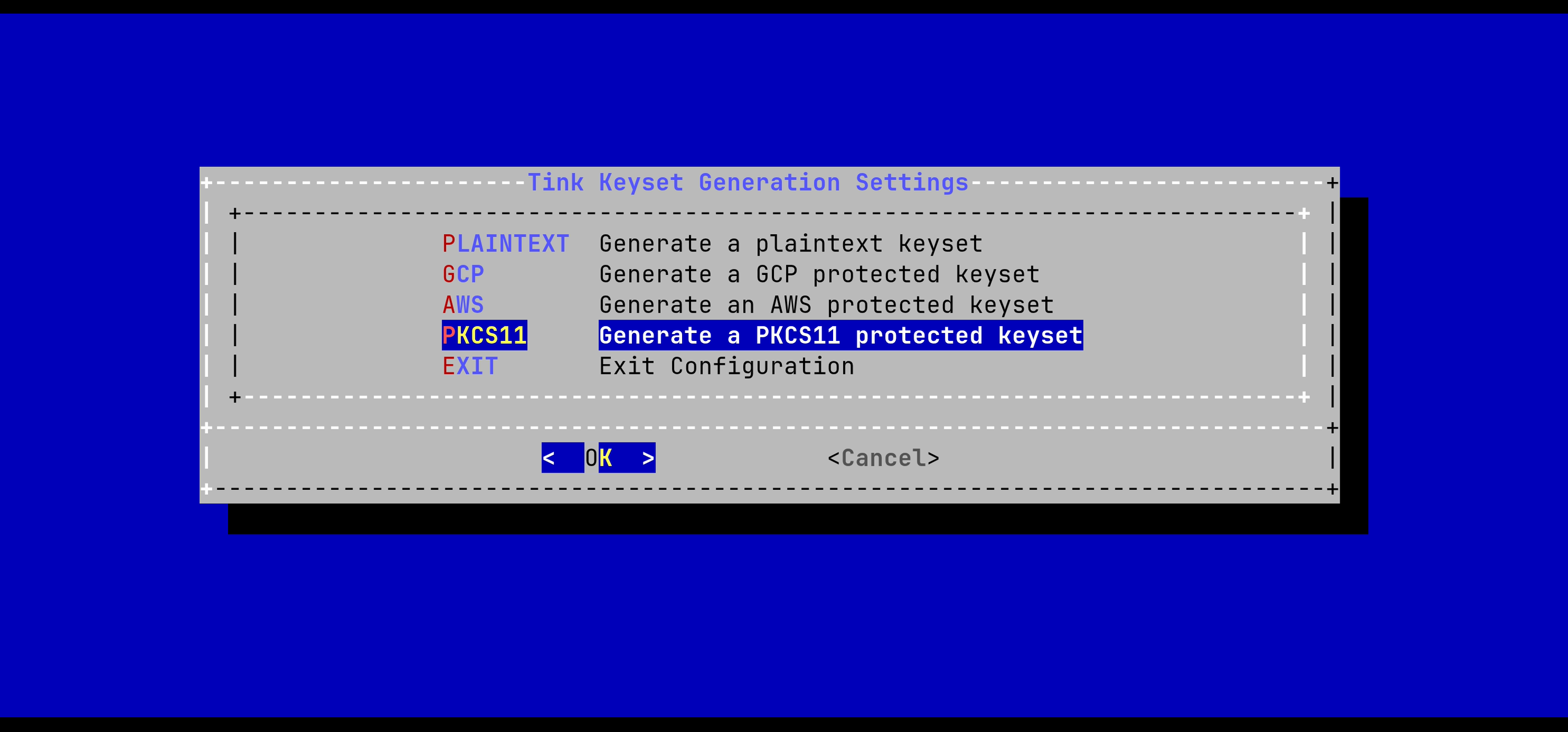
In the Stream menu, select 'HORIZON_TINK_KEYSET':
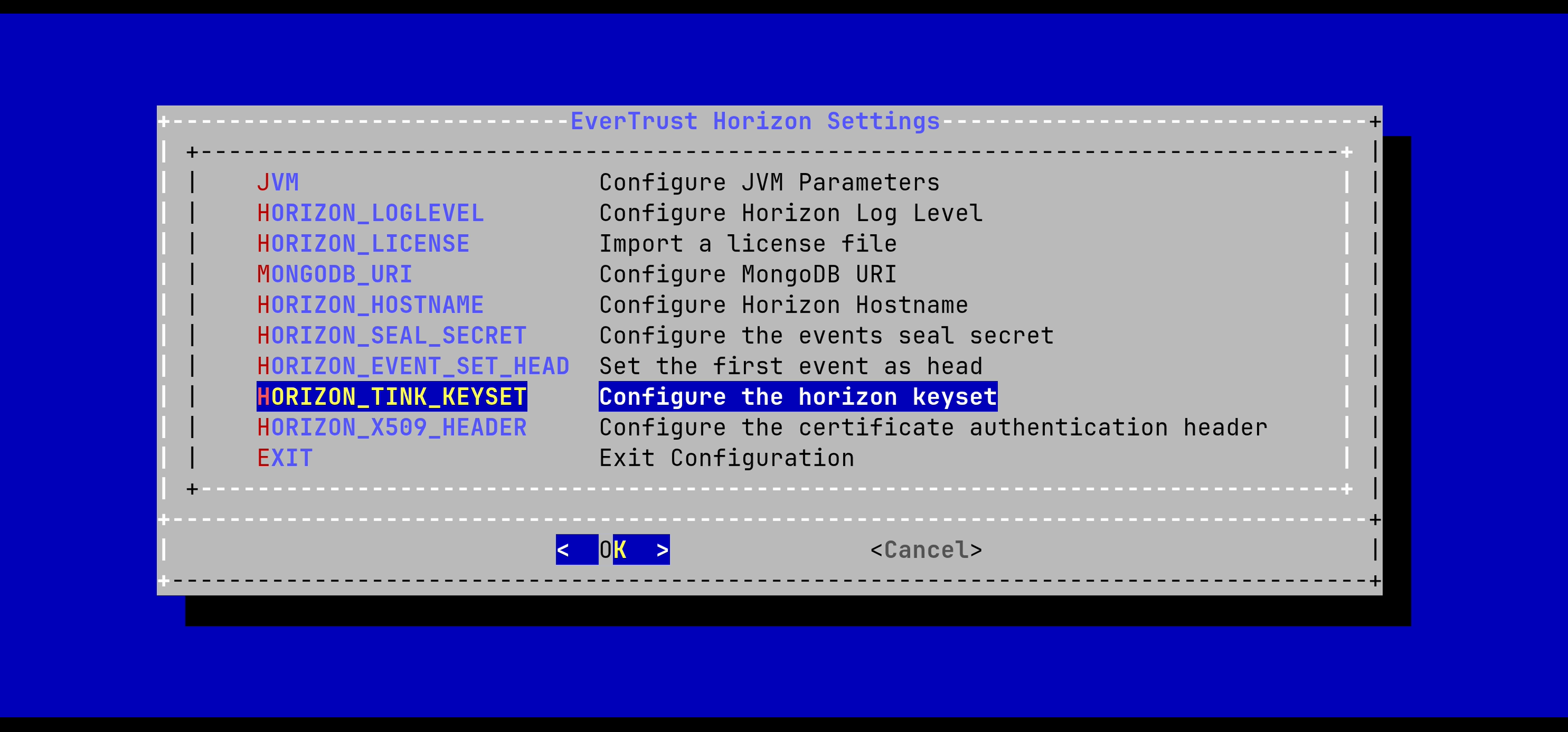
Generating a plaintext keyset
In the Tink Keyset Generation menu, select 'PLAINTEXT':
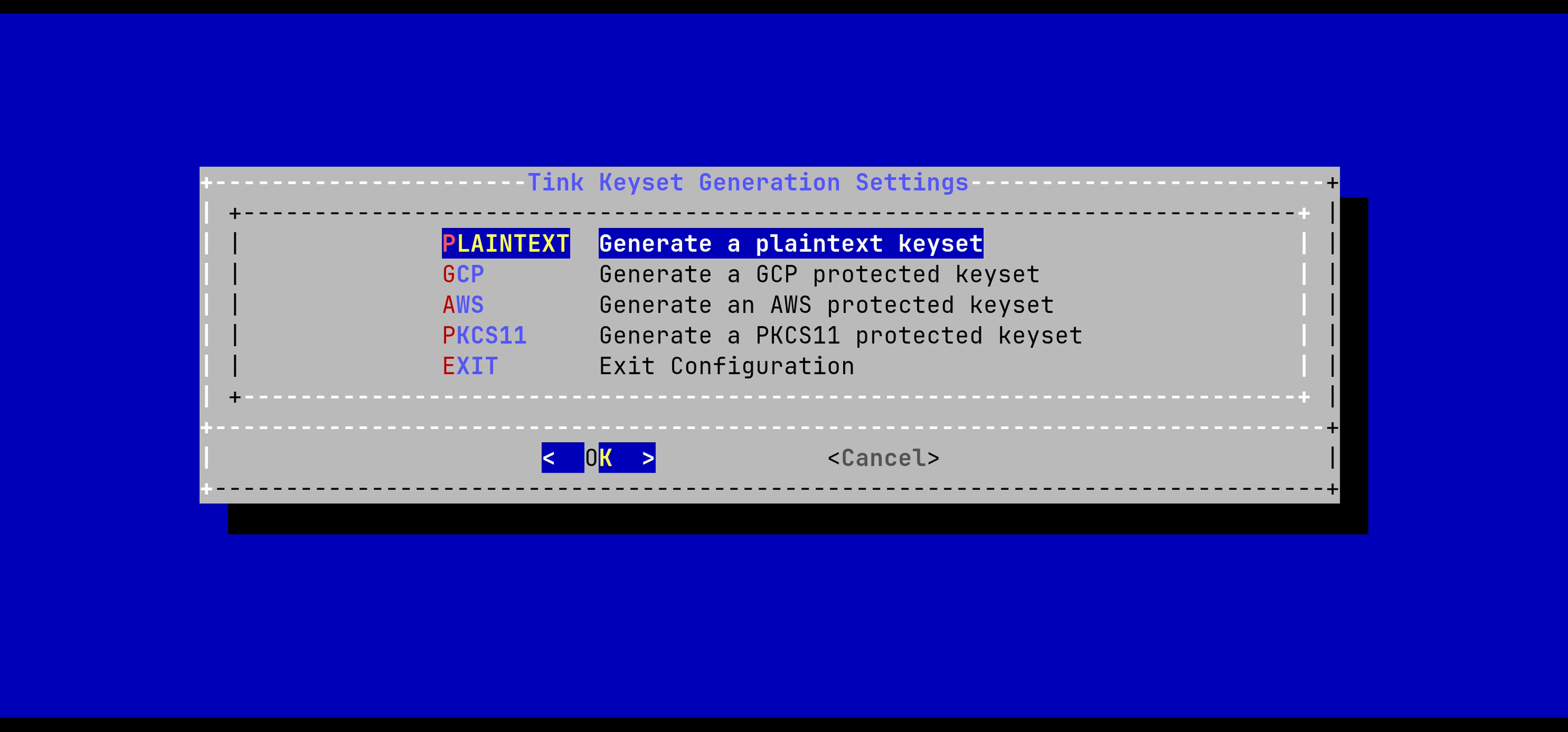
The keyset will be generated automatically.
For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonGenerating a GCP protected keyset
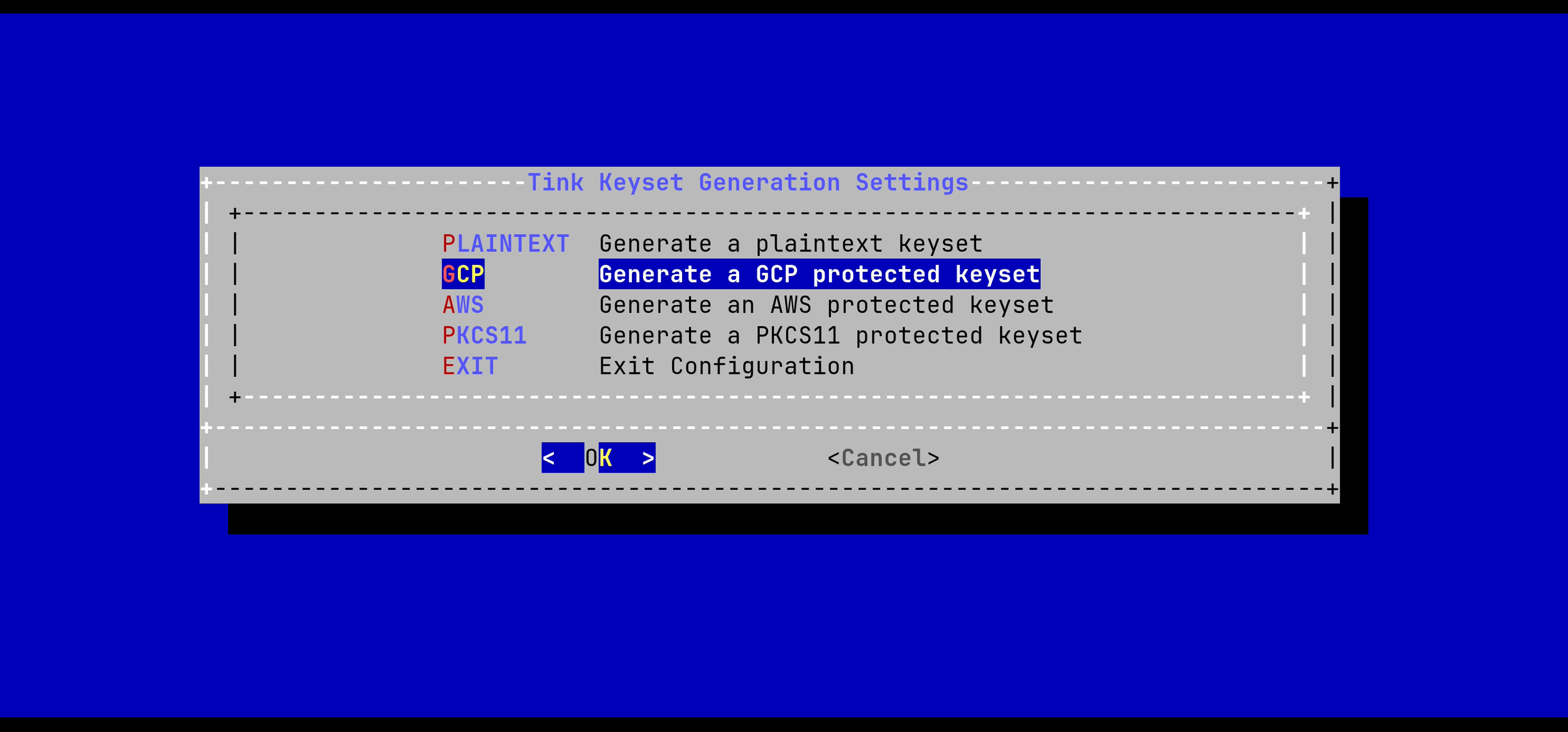
In the Tink Keyset Generation menu, select 'GCP':
The URL of the GCP master key must be typed in the menu. Path to a credentials file can be specified if not using the default SDK path.
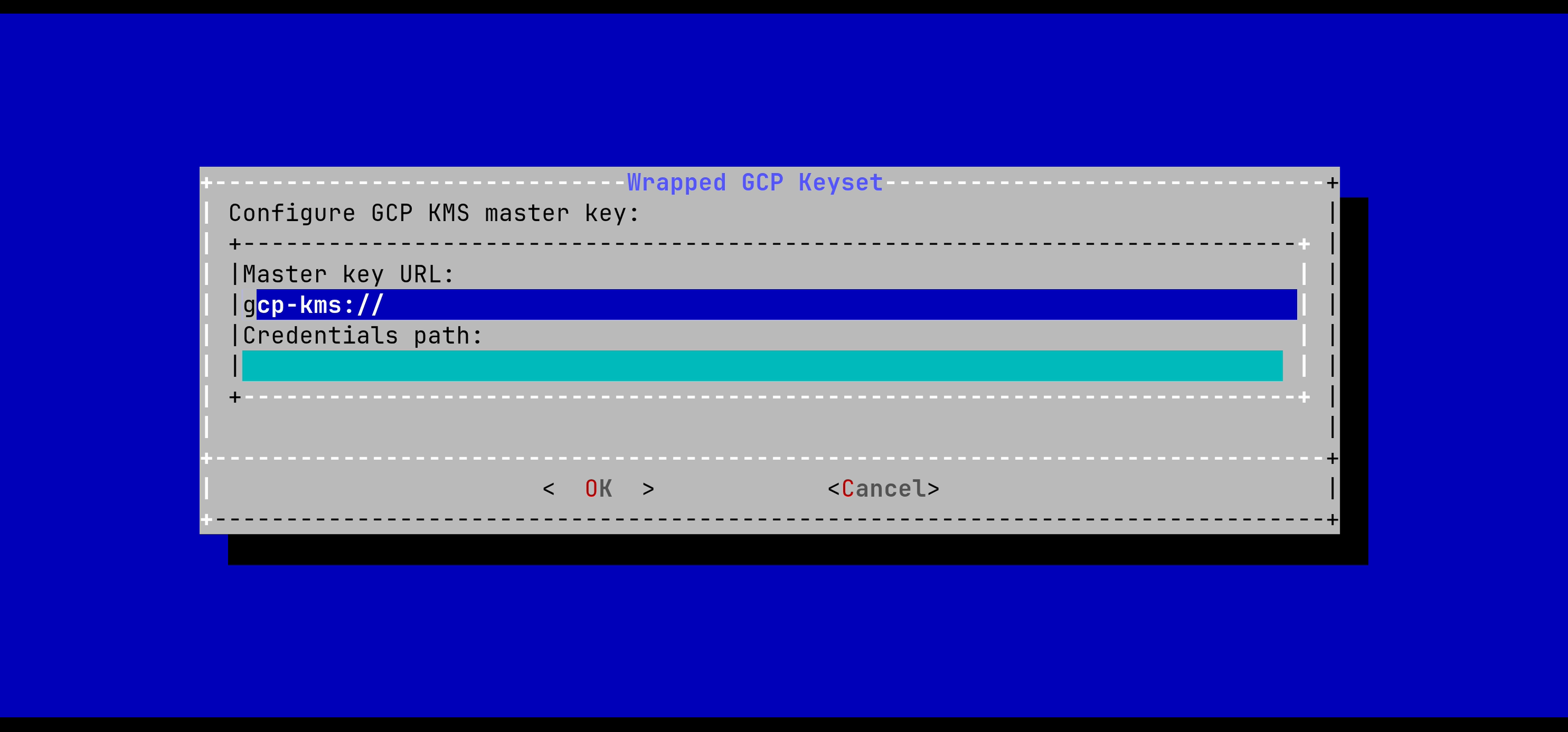
After pressing OK, the keyset will be generated automatically.

For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonGenerating an AWS protected keyset
In the Tink Keyset Generation menu, select 'AWS':
The URL of the AWS master key must be typed in the menu. Path to a credentials file can be specified if not using the default SDK path.
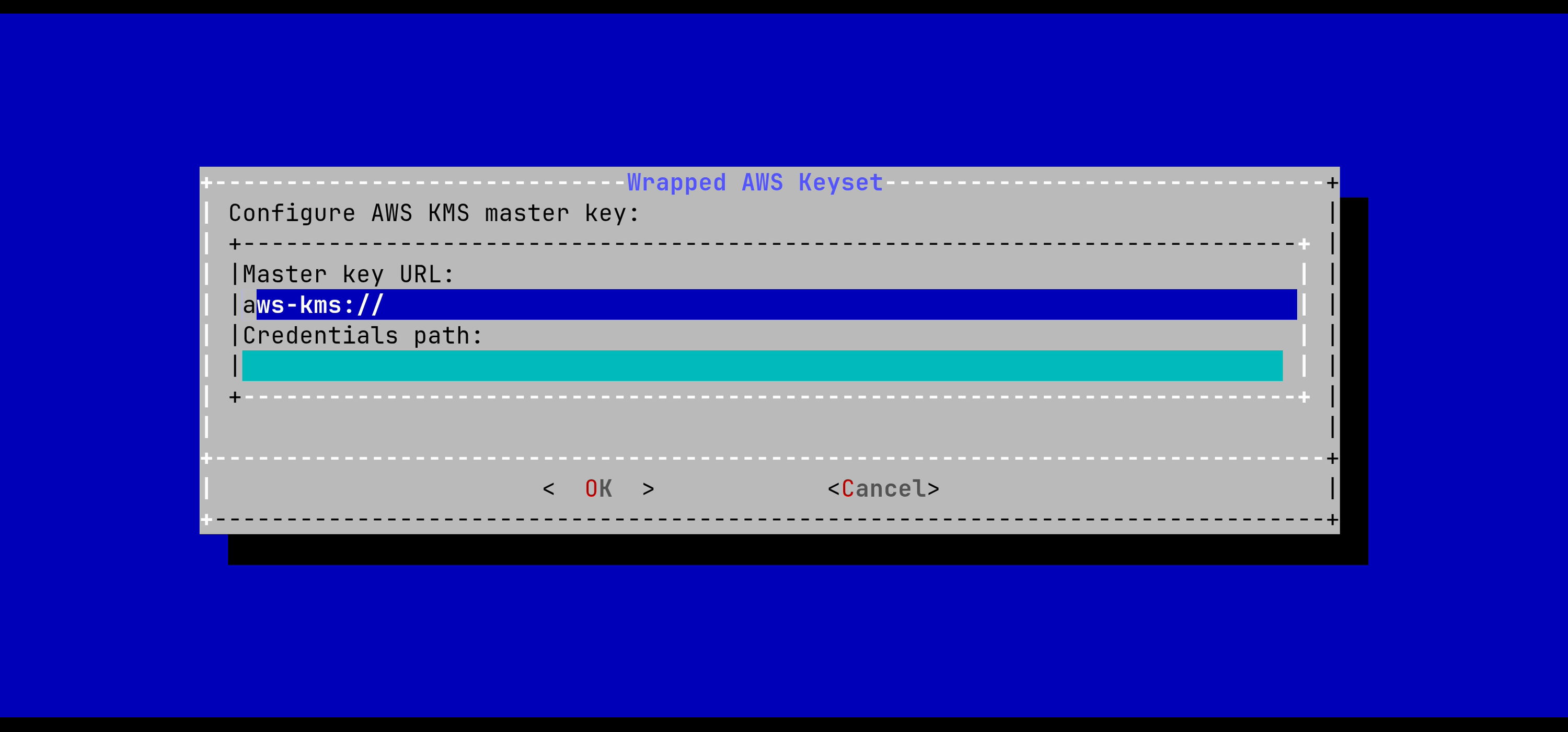
After pressing OK, the keyset will be generated automatically.

For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonGenerating a PKCS#11 protected keyset
In the Tink Keyset Generation menu, select 'PKCS11':
The URL of the PKCS#11 master key must be typed in the menu.
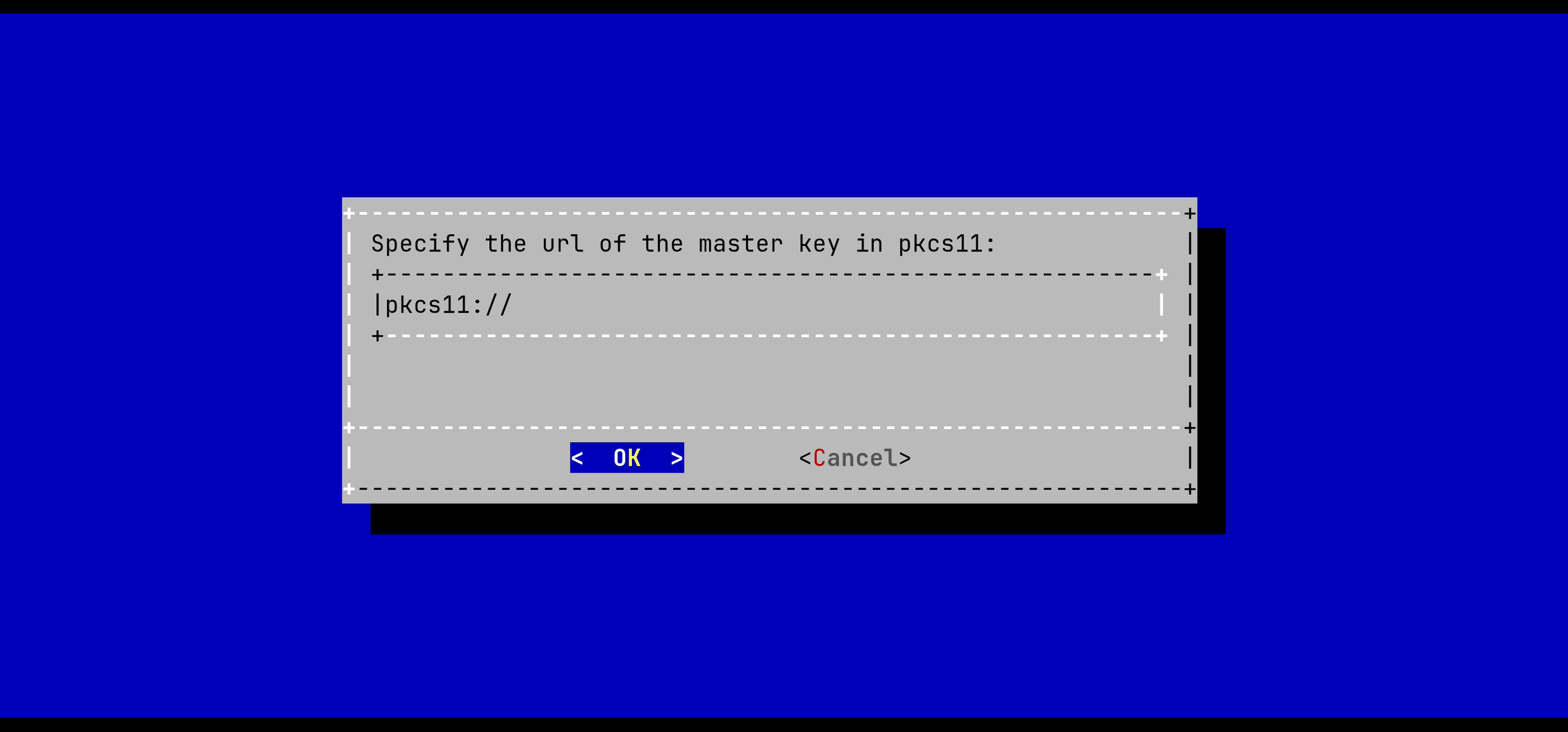
The expected format is:
pkcs11://object=<object name>;type=<object type>;slot-id=<slot id>?module-path=<library path>&pin-value=<pin>;
Example:
pkcs11://object=kek;type=secret-key;slot-id=-1?module-path=/usr/lib/softhsm/libsofthsm2.so&pin-value=1234";
After pressing OK, the keyset will be generated automatically.

For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonInstalling Horizon on a cluster of servers
| This section must not be followed if you plan on deploying Horizon in standalone mode (vs cluster mode). WARNING: This section does not explain how to install Horizon on a Kubernetes cluster. Please refer to the dedicated section. |
In the main menu, select 'Pekko_Play':

In the Pekko_Play menu, select 'PEKKO_HA':

In this menu, specify either the IP address or the DNS name for each server that will be running Horizon on this cluster, as well as the local node index (the number of the node that you are configuring at that moment). You must also specify where the port Artery is hosted, usually it should be on the same node with a different port.
|
Note that the local node index must match the Node Hostname parameter: |

Save your changes from the menu.
The High Availability mode is now configured on the current node:

You must now configure your other nodes, but because they belong to the same cluster they need to share the same secret, the same secret seal event, the same hostname and the same database.
In order to be able to do that, you need to copy the configuration file that was generated by the horizon-config app, named /etc/default/horizon and paste it on each one of your nodes;
Then on each other node, run the Horizon Configuration utility:
Connect to the server with an account with administrative privileges;
Start the Horizon configuration utility by running:
# /opt/horizon/sbin/horizon-config
In the Pekko_Play menu, select 'PEKKO_HA':

Here, you need to change the local node index to match the hostname of the node that you are configuring:

You will need to import the Horizon license file on each node manually, following the guidelines of section Installing the Horizon license, as well as copying the keyset in /opt/horizon/etc/horizon.keyset.
|
Additionally, on each node, you will need to open the ports used for Pekko_HA and Pekko_MGMT, which are by default 17355 and 7626:
-
RHEL
-
Debian
$ firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=17355/tcp $ firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=7626/tcp
Reload the firewall configuration with:
$ systemctl restart firewalld
If you are using a specific firewall, make sure to open these ports.
For the changes to take effect, you must restart the Horizon service by running:
# systemctl restart horizonEnabling the lease
To allow for High Availability even when a minority of nodes are up, the following configuration should be added (reference).
pekko.cluster.split-brain-resolver {
active-strategy = "lease-majority"
lease-majority {
lease-implementation = "lease.mongo"
}
}